Latin America is filled with ancient cultures. These cultures thrived before Europeans arrived. The Inca, Maya, and Aztec societies were among the most impressive.
These groups built a strong foundation for today’s culture. Their stories are key to understanding Latin America’s past and present.
A vibrant landscape showcasing ancient ruins of Latin American civilizations, surrounded by lush jungles and majestic mountains, featuring intricate stone carvings and temples, warm sunset lighting casting golden hues, diverse flora and fauna, evoking a sense of exploration and connection to history.
We will look at what these cultures achieved. We’ll see their impact on art, architecture, and farming. Join us as we dive into Latin America’s ancient history and its lasting effects.
Key Takeaways
- Latin America’s ancient cultures influenced the contemporary cultural landscape.
- The Inca, Maya, and Aztec civilizations had significant achievements prior to European contact.
- Understanding pre-Columbian history is vital for grasping modern Latin American identity.
- Indigenous cultures continue to impact various aspects of life in Latin America today.
- Exploring these civilizations reveals their contributions to agriculture, art, and architecture.
Introduction to Latin America’s Diverse Ancient Cultures
Latin America is a mix of many ancient cultures. It shows a rich mix of traditions, languages, and ways of living. Over half a billion people live here, showing a deep cultural heritage.
The Amazon River, the longest coastline, and the Atacama Desert show the area’s varied landscapes. These lands helped grow different crops and animals. This led to the rise of societies based on farming.
Geography and resources shaped these cultures. Central America, the Southern Cone, and the Caribbean have their own cultures. Over fifty states in Central America and Mexico speak Spanish.
There are about 250 indigenous societies left today. They show the strength of these ancient cultures.
The Mayans lived from 250 to 900 AD. They made big contributions, like writing and buildings. Their work still shapes our world today.
The mix of nature and culture in Latin America is complex. It shows the rich history of ancient societies. This history still affects us today.
Mesoamerican Civilizations: A Snapshot
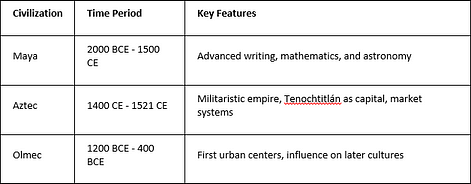
Mesoamerican history and culture are rich and complex. They show the amazing achievements of ancient civilizations. The Maya, Aztec, and Olmec civilizations made big contributions to human development and society.
These cultures traded and shared practices. Yet, each had its own traditions and innovations.
Overview of the Maya, Aztec, and Olmec Civilizations
The Maya civilization started around 2000 BCE. They lived in the jungles of Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras. They were known for their writing, calendars, and step pyramids.
The Aztec civilization was in central Mexico from the 14th to the 16th centuries. They ruled over 500 small states and 5 to 6 million people. Their capital, Tenochtitlán, was very crowded.
The Olmec civilization was the “mother culture” of Mesoamerica, starting around 1150 BCE. They built the first urban centers and influenced later cultures. Their legacy lived on through the Maya and Aztecs.
Significance of Rituals and Beliefs
Rituals and beliefs were key in Mesoamerica. For the Maya, ceremonies were tied to the sky, farming, and ancestors. They used calendars to plan rituals.
The Aztecs had big ceremonies, including human sacrifice. They believed these rituals kept the sun up and crops fertile. Priests played a big role in these rituals.
The Olmecs also had rituals, like shamanistic practices and worship of deities in their art. These rituals were important for community and identity.
Inca Empire: Engineering Marvels of the Andes
The Inca Empire was a marvel of engineering. It thrived from 1400 to 1533 CE. Machu Picchu is a key example of their skill.
This site is in the Andes Mountains. It amazes visitors with its stonework and how it fits into the landscape.
Machu Picchu: The Citadel of Wonder
Machu Picchu is known as the “Lost City of the Incas.” It shows the Incas’ engineering skills. The stones fit together so well, they’ve lasted for centuries.
It has buildings, terraces, and farming systems. These show how the Incas farmed at high altitudes.
Machu Picchu was more than just a city. It was a royal estate and a religious site. Its buildings were aligned with the stars.
People from all over visit. They come to see the history and architecture of the Inca Empire.
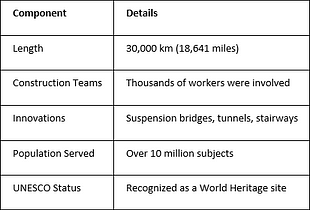
The Inca Network of Roads and Communication
The Inca Road System was over 30,000 km long. It connected communities from Colombia to Argentina. It helped with trade and communication.
Some of these roads are still used today. This shows how well they were built.
This system helped move goods, information, and armies. It showed the empire’s administrative skill. Roads from Cusco managed the empire’s territories well.
The legacy of Inca engineering still inspires today. It encourages us to explore the ancient world through their roads.
Exploring the Rich Heritage of Latin America’s Ancient Culture
Latin America’s ancient culture is a mix of many influences. It combines indigenous traditions with Spanish, Portuguese, African, and Asian elements. This blend has had a big impact on today’s Latin American society.
Art and architecture show off this rich heritage. Places like the Maya pyramids and Incan cities tell stories of the past. They inspire art today.
Social customs have changed over time but still connect to the past. Festivals celebrate old traditions. Food, like tamales and empanadas, shows how cultures mix.
Language is key to keeping culture alive. Spanish is common, but many Amerindian languages also exist. They keep ancient stories and wisdom alive.
Knowing about the past is important today. It helps us appreciate the mix of cultures in Latin America. By honoring their heritage, communities celebrate their unique stories and add to the world’s history.
Iconic Archaeological Sites in Latin America
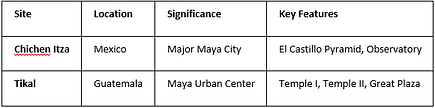
Exploring ancient sites in Latin America shows us the rich past of old civilizations. Chichen Itza and Tikal are two key places. They show the Maya’s skill in building and understanding the world.
Chichen Itza: A Maya Masterpiece
Chichen Itza is in the Yucatan Peninsula. It’s a UNESCO World Heritage site. The El Castillo pyramid shows the Maya’s knowledge of the stars.
On equinoxes, a shadow looks like a snake on the stairs. This shows how the Maya mixed architecture with the sky. Visitors see amazing buildings and learn about the Maya’s history.
Tikal: The Heart of the Maya Empire
Tikal is in Guatemala’s jungle. It’s a huge site with big temples and carvings. It was a key city for trade and politics.
Here, nature and history meet. Visitors see animals and explore old paths and buildings.
The Intriguing Nazca Lines: Art in the Desert
The Nazca Lines are amazing ancient art in southern Peru. They cover over 80 kilometers (50 miles) with thousands of figures. The Nazca people made them between 500 BCE and 500 CE.
These designs show a deep cultural meaning. Many wonder about the Nazca lines’ purpose.
Aerial view of the Nazca Lines etched into the arid Peruvian desert, showcasing intricate geometric patterns and large animal figures, surrounded by a vast, sunlit landscape with distant mountains under a clear blue sky, emphasizing the contrast between the light beige soil and the deep lines.
Theories Behind the Design and Purpose
Many theories exist about the Nazca Lines. Some think they align with stars and planets. Others believe they were for rituals or farming.
The lines are only four to six inches deep. This makes people wonder how they were made without flying.
The Nazca civilization was smart, even without flying. They made Lines and Geoglyphs of Nasca and Palpa. These show many designs, adding to the mystery.
Since 1994, the Nazca Lines are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Efforts protect them from harm. This includes stopping vandalism and fighting climate change.
Indigenous Cultures of Latin America and Their Legacy
The rich legacy of indigenous cultures in Latin America is still alive today. They show how old traditions and beliefs shape our world now. By keeping their languages and customs alive, they prove their lasting importance.
As new ideas mix with old ones, keeping traditions is key. It helps keep cultural identity strong in today’s world.
Preservation of Traditions and Languages
Keeping traditions alive is crucial for indigenous communities. They work hard to save their ancient languages. These languages hold their stories, history, and identity.
They use workshops, language programs, and festivals to keep their languages alive. This lets young people connect with their roots.
Contemporary Influences of Ancient Cultures
Today, modern culture is influenced by indigenous traditions. Old art forms like textiles and music are seen in new ways. This mix of old and new sparks a lively cultural scene.
Modern activism also takes cues from indigenous views. It tackles big issues like land rights and saving the environment. This blend of old and new ideas celebrates history while embracing change.
Archaeological Discoveries: Uncovering the Past
Recent finds in Latin America have given us a peek into the past. They show how ancient groups were connected. We learn about their lives, beliefs, and how they traded with others.
Recent Findings in South America
Excavations in South America keep bringing us amazing news. The discovery of Machu Picchu in 1911 was a big deal. It led to more study of this site.
La Ciudad Perdida, found in Colombia, is another big find. It shows the life of the Tayrona people. To see it, you have to trek through jungles for four days.
Implications for Understanding Ancient Civilizations
These finds help us understand ancient groups better. The Moai statues on Easter Island show the Rapa Nui people’s skills. They also show their complex society.
Archaeology and national identity are closely linked. Local and foreign experts work together. This teamwork shows that cultural heritage knows no borders.
As we keep learning, our views on the past change. We see ancient people in a new light. Their legacy helps us today, teaching us about heritage and identity.
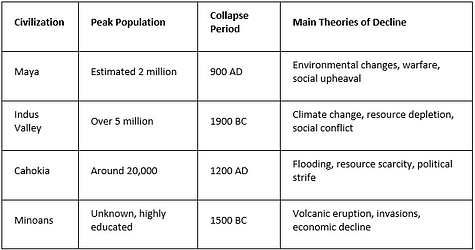
Unsolved Mysteries of Lost Civilizations
The fall of ancient societies is a big mystery. Places like Mesoamerica left clues that puzzle us. To understand why they vanished, we look at many reasons.
Theories Surrounding the Collapse of Mesoamerican Societies
Many theories try to explain why Mesoamerica’s great civilizations fell. The Maya, known for math and building skills, declined around 900 AD. Theories include:
-
Environmental Changes: Long droughts might have hurt farming, causing food shortages.
-
Warfare: Wars between city-states could have broken trade and power.
-
Social Upheaval: A gap between rich and poor might have caused trouble.
Other lost civilizations also have mysteries. The Indus Valley Civilization, for example, had big cities but vanished around 1900 BC. Cahokia, with 20,000 people, was hit by floods around 1200 AD.
Many theories exist for each lost culture. These stories keep archaeologists busy, showing how important it is to learn about these civilizations.
Cultural Heritage and Its Importance Today
The cultural heritage of Latin America is a vibrant tapestry. It is made from the rich histories and traditions of ancient civilizations. This heritage is not just in the past. It shapes modern identity across the continent today.
Impact on Modern Latin American Identity
In today’s Latin America, ancient cultures’ influence is seen everywhere. Festivals, art, and community practices show respect for latin american heritage. Celebrations like Latin American Heritage Month grow from a week to a month-long tribute.
Institutions like the Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) promote cultural heritage. They have exhibits like “We Live in Painting: The Nature of Color in Mesoamerican Art.” This show runs until September 15, 2025, and features over 270 artifacts from Mesoamerican societies.
The LACMA exhibition shows a wide range of items, from clay vessels to textiles. Colors like red hold deep spiritual meanings in Mesoamerican cultures. These exhibits help us see how cultural heritage shapes our identities today.
Modern societies in Latin America celebrate their ethnic diversity. The Mexican Constitution calls the nation “pluricultural.” This shows a mix of ancient and modern influences. Knowing the importance of cultural heritage helps us understand identity in the region today.
Exploration and Tourism: Connecting with Ancient Cultures
Tourism in Latin America is growing fast. More people want to see the ancient cultures. This lets them get close to old sites and learn from local communities.
It’s important to do this in a way that respects the culture and helps the environment. This makes the trip better for everyone.
Ethical Tourism Practices
Visitors should follow rules to respect local cultures at archaeological sites. Here are some ways to do it:
-
Engaging with Local Guides: Choose tours with local guides. They share their knowledge and help the community.
-
Respecting Cultural Norms: Learn and follow local customs. This shows respect for the community.
-
Supporting Local Businesses: Pick places to stay and eat that are owned by locals. It helps the local economy.
-
Avoiding Overcrowding: Visit during less busy times. It’s better for the site and the community.
Recommendations for Visitors to Archaeological Sites
Here are tips to enjoy ancient cultures without harming them:
-
Research Before You Go: Knowing the site’s history makes your visit more special.
-
Participate in Community Events: Join cultural festivals. It’s a great way to learn and have fun.
-
Practice Sustainable Travel: Follow tips to reduce waste and protect nature.
-
Leave No Trace: Don’t damage the site or environment. Avoid graffiti and don’t climb on sacred places.
By following these tips, visitors can help preserve ancient cultures. This makes the trip better for everyone and supports sustainable tourism in Latin America.
Literature and Myths of Ancient Civilizations
The literature of ancient civilizations is full of cultural insights and beliefs. It shows us how societies viewed the world. Myths in Latin America, kept alive through stories, help us understand indigenous cultures.
These stories connect old values with today’s life. They are a bridge from the past to now.
Preservation of Oral Traditions
Oral traditions give us a peek into the thoughts of ancient peoples. Many stories were written down by friars and chroniclers during conquest times. The 15th century saw more writing, thanks to the Spanish Empire.
Places like Lima’s school in 1551 helped grow literature. Mexico City became a center for writers, influenced by Europe.
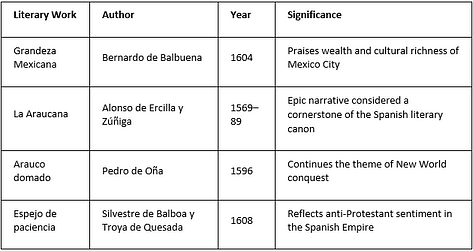
Important writers like Francisco de Terrazas emerged. His work added to the growing literary scene. “Grandeza mexicana” by Bernardo de Balbuena celebrated Mexico City’s wealth.
Alonso de Ercilla y Zúñiga’s “La Araucana” is a key work in Spanish and Latin American literature. Pedro de Oña’s “Arauco domado” and Silvestre de Balboa y Troya de Quesada’s “Espejo de paciencia” showed the conflicts and passions of their time.
These stories and writings keep the legacies of ancient civilizations alive. They enrich our understanding of Latin America’s rich cultural heritage.
A vibrant scene depicting a gathering of ancient storytellers around a roaring fire, surrounded by lush jungle vegetation. The storytellers, dressed in traditional attire, convey rich oral traditions through expressive gestures and animated faces. Ethereal wisps of colorful, swirling imagery rise from the fire, illustrating mythical creatures and legends of ancient civilizations. The night sky glimmers with stars, adding a mystical ambiance to the cultural heritage being shared.
Conclusion
Latin America’s ancient culture is full of life and history. It shows us the amazing work of the Inca Empire and the Amazon’s green beauty. These cultures have greatly influenced our world today.
Indigenous groups have shown great strength and care for nature. They live well with the environment, even with today’s big challenges.
Knowing about these cultures helps us understand Latin America today. The Aymara and Quechua people teach us about keeping traditions alive. Famous authors also share stories of this rich history.
We must protect these cultures and fight for the rights of indigenous people. More people are learning about and loving Latin America’s ancient ways. This helps keep our heritage alive for the future.
Ready to bring the vibrant history of Latin America's ancient civilizations to life? Dive deeper into the fascinating worlds of the Inca, Maya, and Aztec with our meticulously crafted coloring book. Perfect for history enthusiasts, artists, and learners of all ages, this book offers a creative journey through time. 🌟
Get your copy now and start coloring your way through the captivating stories and achievements of Latin America's greatest cultures. Let the adventure begin!
Thank you!